Scientific research has shown that a
decline in intracellular Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+) levels is
associated with aging and age-related diseases. In animal models, therapeutic
strategies aimed at increasing NAD+ levels have been effective in delaying or
preventing such conditions. Numerous studies also suggest that supplementation
with NAD+ precursors such as Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) can elevate NAD+
levels in the body, thereby improving cellular energy metabolism and
alleviating age-associated functional decline.
The First Human Clinical Trial on NMN
Safety
To evaluate the safety of NMN supplementation in humans, the first human clinical trial was conducted by Keio
University School of Medicine in Japan. The study began in 2016, and its
findings were published in 2019. This trial aimed to assess the clinical safety
of a single dose of NMN by monitoring clinical and metabolic parameters in
healthy Japanese men.

Study Overview
Title: Oral Administration of Nicotinamide
Mononucleotide (NMN) Increases Nicotinamide Metabolism in Healthy Men: A
Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Parallel-Group Trial
Institution: Keio University, Japan
Study Start Date: 2016
Publication Date: 2019
Participants: 10 healthy Japanese men aged
40–60
Intervention: Single-arm, non-randomized intervention with a one-week washout period between doses. Each participant received a single oral dose of 100 mg, 250 mg, and 500 mg NMN. Clinical and pharmacokinetic parameters were assessed over a 5-hour period after each administration.
Conclusion: A single oral dose of up to 500
mg NMN was well-tolerated in healthy adult men, without causing significant
adverse effects. NMN was efficiently metabolized.
Clinical Parameters
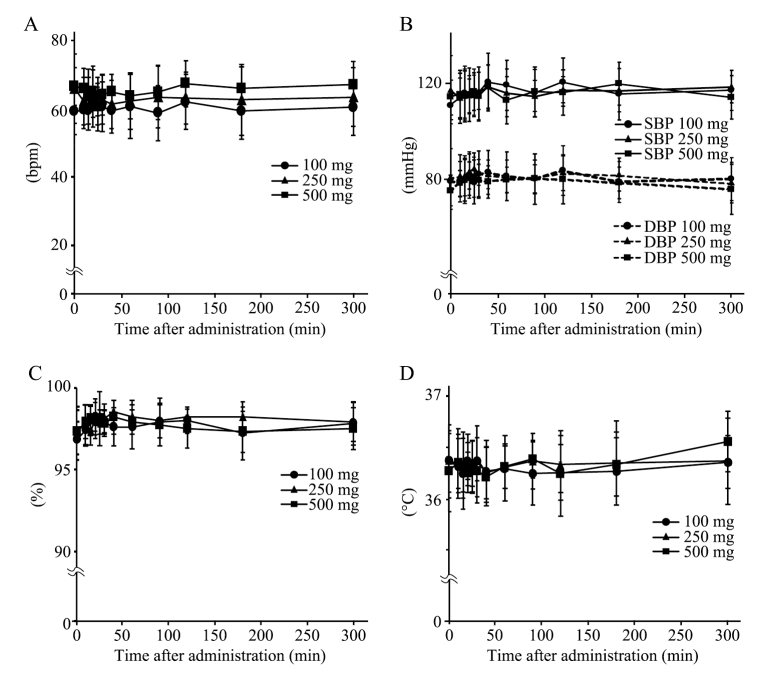
The study showed no significant clinical
symptoms or changes in key vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure,
oxygen saturation, or body temperature following NMN administration.
Serum Biomarkers
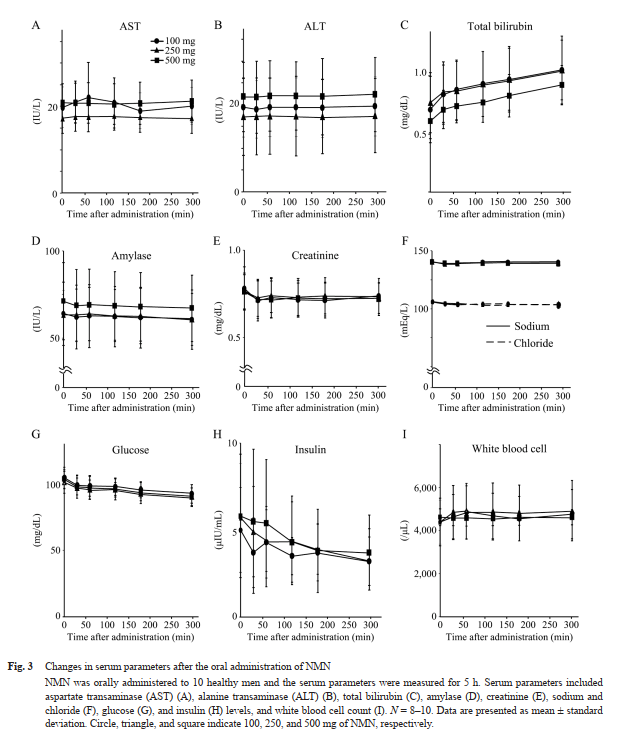
Laboratory results indicated that serum bilirubin slightly increased, while creatinine, chloride, and glucose levels slightly decreased. However, all values remained within normal physiological ranges and were not dose-dependent.
Plasma Metabolite Profile
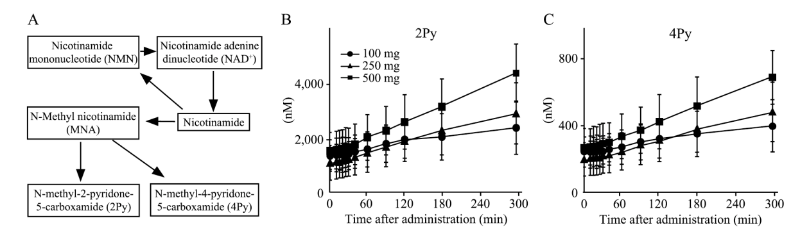
Post-administration plasma levels of NMN metabolites— namely, N-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide (2Py) and N-methyl-4-pyridone-5-carboxamide (4Py)—increased in a dose-dependent manner, indicating effective absorption and metabolism of NMN.
Ophthalmic Evaluation
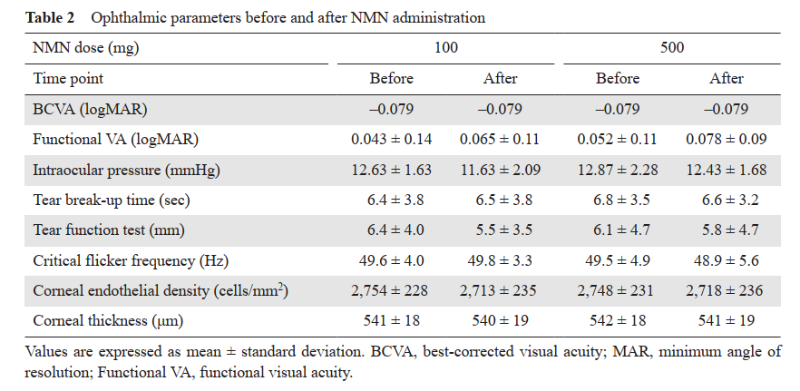
Ophthalmological examinations conducted before and after NMN intake showed no significant differences across all doses. No adverse effects on visual function, optic nerve, or retinal health were observed.
Summary
This pioneering human clinical study confirms that oral NMN supplementation at doses up to 500 mg is safe and well-tolerated in healthy adult males. It also provides pharmacokinetic data supporting efficient metabolism of NMN in humans.
About Leadsynbio
At Leadsynbio, we believe that product efficacy begins with safe and consistent raw materials. As a synthetic biology-based manufacturer, we have innovated a fully enzymatic NMN production process that is green, efficient, and industrially scalable. Our platform enables us to supply NMN ingredients with high purity and batch-to-batch consistency, ensuring a solid foundation for clinical and commercial applications.
Next:NMN in Skincare: Decoding the Science and Scaling Commercial Innovation
Prev:How Much NMN Should You Take? A Review of Global Clinical Trials

Suzhou Leadsynbio Technology Co.,Ltd. is honored to be recognized inthe Hurun Future Unicorns – China Cheetahs Index 2025. This prestigious list spotlights our continued commitment to innovation and excellen...
[ Details ]Feb 09,2026