Sleep disorders refer to abnormal sleep duration or unusual behaviors during sleep, reflecting disruptions in the normal rhythm between sleep and wakefulness.
According to the China Sleep Big Data Report 2023, the incidence of insomnia among Chinese adults has reached 38.2%, with more than 510 million people affected by sleep disturbances. Meanwhile, about 10–15% of U.S. adults suffer from chronic insomnia, and up to two-thirds experience occasional insomnia symptoms, as reported by the Sleep Foundation.
Research indicates that chronic sleep disorders are one of the major causes of chronic fatigue syndrome, hypertension, coronary heart disease, diabetes, and cerebrovascular diseases. They can quadruple the risk of stroke and sharply increase the likelihood of obesity and cancer.[1]
Multiple human clinical trials conducted both domestically and internationally have demonstrated that supplementing with NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) can significantly improve sleep quality and reduce sleep onset latency (the time it takes to fall asleep).
1. University of Tsukuba, Japan: NMN Reduces Sleepiness and Fatigue
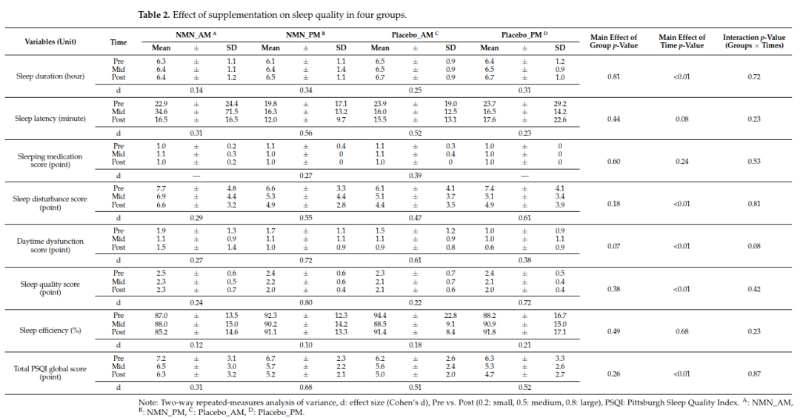
In February 2022, a clinical trial led by the University of Tsukuba in Japan published results showing that daily supplementation with 250 mg of NMN effectively improved lower limb function in older adults and reduced feelings of drowsiness and fatigue, with better results when taken in the afternoon.
The study enrolled 108 Japanese adults aged 65 and older in a 12-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Researchers evaluated the effects of NMN on sleep quality, fatigue, and physical performance using the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), the “Jikaku–Shoshirabe” self-awareness questionnaire, as well as grip strength, sit-to-stand tests, start timing, and 5-meter habitual walking speed.
Results showed that participants in the NMN group achieved significantly higher PSQI scores. Notable interactions were observed between NMN intake and improved 5-times sit-to-stand (5-STS) performance and reduced daytime sleepiness. The NMN group exhibited the largest effect sizes for 5-STS, Timed Up & Go (TUG), and sleepiness reduction.[2]
2. Doshisha University, Japan: NMN Improves Sleep in Postmenopausal Women
In June 2022, a research team led by Professor Yonei from Doshisha University published findings in Glycative Stress Research showing that NMN supplementation in postmenopausal women improved various age-related health markers, including metabolic and hormonal health, as well as skin-aging indicators.[3]
Subjective self-assessments further revealed that after eight weeks of oral NMN intake, participants experienced:

3. Southern University of Science and Technology (SUSTech), China: NMN Shortens Sleep Onset Latency
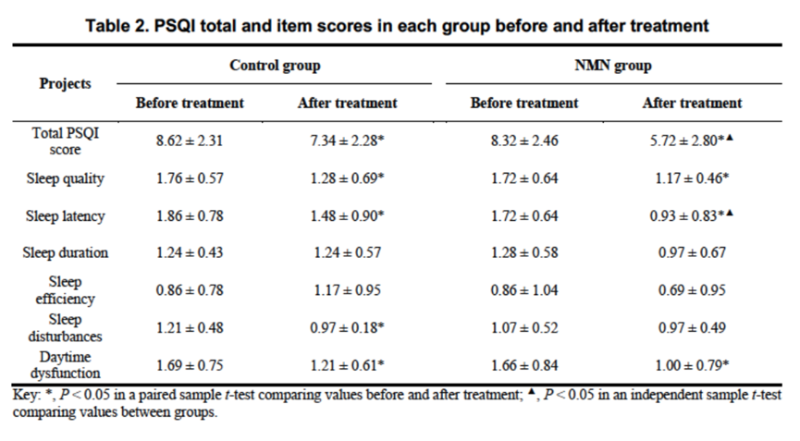
In December 2022, a research team from Southern University of Science and Technology (SUSTech) published a study in the Journal of Translational Medicine showing that NMN significantly shortened sleep latency, increased REM and deep sleep duration, and improved overall sleep quality.[4]
The study involved 58 middle-aged and older adults aged 45–75, who underwent 12 weeks of PSQI assessments. Compared with the placebo group, participants taking NMN scored significantly higher in sleep quality and showed reduced sleep latency.
Data from smart wearables confirmed that the NMN group experienced longer durations of deep sleep and REM sleep during the night.
Summary
These clinical studies consistently demonstrate that NMN supplementation can significantly enhance sleep quality, reduce daytime drowsiness, and promote healthier sleep patterns. By boosting NAD⁺ levels, NMN may also help prevent age-related diseases and physical decline.
Importantly, no adverse effects related to NMN intake were reported in any of the above trials.
References:
[1] Nicholson K, Rodrigues R, Anderson KK, Wilk P, Guaiana G, Stranges S. Sleep behaviours and multimorbidity occurrence in middle-aged and older adults: findings from the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging (CLSA). Sleep Med. 2020;75:156-162. doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2020.07.002
[2]Kim, Mijin, et al. "Effect of 12-Week Intake of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide on Sleep Quality, Fatigue, and Physical Performance in Older Japanese Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Study." Nutrients 14.4 (2022): 755.
[3]Morita, Y., Izawa, H., Hirano, A., Mayumi, E., Isozaki, S., & Yonei, Y. Clinical evaluation of changes in biomarkers by oral intake of NMN. Glycative Stress Research. June, 2022.
[4] ZHAO, B., Liu, C., Qiang, L., Liu, J., Qiu, Z., Zhang, Z., Zhang, J., Li, Y., & Zhang, M. (2022). Clinical observation of the effect of nicotinamide mononucleotide on the improvement of insomnia in middle-aged and old adults. American Journal of Translational Medicine, 6(4), 167–176.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for educational purposes and does not constitute medical or commercial advice. Information is derived from publicly available sources. Any reproduction, publication, or citation requires prior written consent from Leadsynbio.

Suzhou Leadsynbio Technology Co.,Ltd. is honored to be recognized inthe Hurun Future Unicorns – China Cheetahs Index 2025. This prestigious list spotlights our continued commitment to innovation and excellen...
[ Details ]Feb 09,2026