Obesity and Diabetes: A Growing Concern
Obesity is a serious health condition—both a disease itself and a major contributor to multiple metabolic disorders. Among these, diabetes is one of the most common complications.
In China, ~500 million people are prediabetic → ~1 in 3 adults is at risk of developing diabetes.
Key mechanism: Insulin resistance is a
primary driver of prediabetes.
What is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin resistance (↓ insulin sensitivity) occurs when cells respond poorly to insulin.
Glucose uptake is impaired → blood sugar rises
Can progress to type 2 diabetes if unchecked
Visual cue: Insulin resistance → “key not fitting the lock” → glucose can’t enter cells efficiently.
NMN Enhances Skeletal Muscle Insulin Sensitivity
Study Overview
Type: Randomized, double-blind, 10-week human clinical trial
Outcome measures:
Body composition

NMN Increases NAD⁺ Turnover
Peripheral blood mononuclear cell NAD⁺ levels ↑ in NMN group vs placeboVisual cue: NMN → NAD⁺ “recycling speed ↑” → better metabolic efficiency
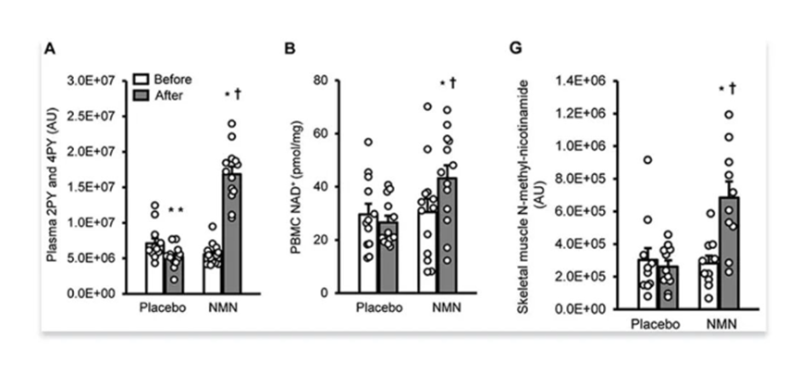
NMN Improves Muscle Insulin Sensitivity
Muscle biopsies analyzed for:Visual cue: Muscle cells respond better to insulin → glucose uptake ↑
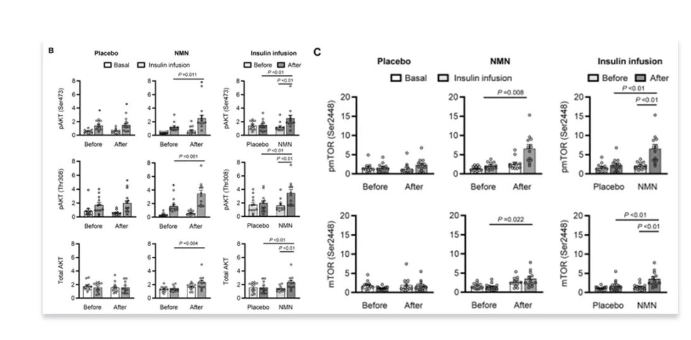
Effects on Skeletal Muscle Biology
RNA sequencing of quadriceps muscle → identified differentially expressed genes (DEGs)Visual cue: NMN → PDGF pathway activation → insulin signaling ↑
Clinical Significance
NMN supplementation (250 mg/day) enhances skeletal muscle insulin signalingKey takeaway: NMN could be a promising strategy for metabolic health support.

References
1.Li Y, Teng D, Shi X, et al. Prevalence of diabetes recorded in China using 2018 diagnostic criteria from the American Diabetes Association: national cross sectional study. BMJ. 2020;369:m997.
2.Mihoko Yoshino et al. Science. Nicotinamide mononucleotide increases muscle insulin sensitivity in prediabetic women. DOI:10.1126/science.abe9985
3.M. Razmara, C. H. Heldin, J. Lennartsson, Platelet-derived growth factor-induced Akt phosphorylation requires mTOR/Rictor and phospholipase C-γ1, whereas S6 phosphorylation depends on mTOR/Raptor and phospholipase D. Cell Commun. Signal. 11, 3 (2013).
Disclaimer: This article is intended for educational purposes and does not constitute medical or commercial advice. Information is derived from publicly available sources. Any reproduction, publication, or citation requires prior written consent from Leadsynbio.

Suzhou Leadsynbio Technology Co.,Ltd. is honored to be recognized inthe Hurun Future Unicorns – China Cheetahs Index 2025. This prestigious list spotlights our continued commitment to innovation and excellen...
[ Details ]Feb 09,2026