Introduction The human body contains more than 600 muscles, with skeletal muscle being the most abundant. Around the age of 40, skeletal muscle mass and strength begin to decline, and this decline can accelerate after age 50. By the time individuals reach 60 years old, chronic muscle lo......
The human body contains more than 600 muscles, with skeletal muscle being the most abundant. Around the age of 40, skeletal muscle mass and strength begin to decline, and this decline can accelerate after age 50. By the time individuals reach 60 years old, chronic muscle loss—also known as sarcopenia—can amount to approximately 30% of total muscle mass [1].
Sarcopenia is not just a cosmetic or lifestyle concern; it is a recognized age-related condition linked to impaired physical function, increased risk of falls, disability, and even mortality [2]. Globally, it is estimated that around 50 million people currently live with sarcopenia, and this number could rise to 500 million by 2050 [3].
NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide) is a biological precursor to NAD⁺ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), a coenzyme essential for cellular energy metabolism. By increasing NAD⁺ synthesis, NMN may help improve muscle cell energy turnover, potentially influencing strength and endurance.
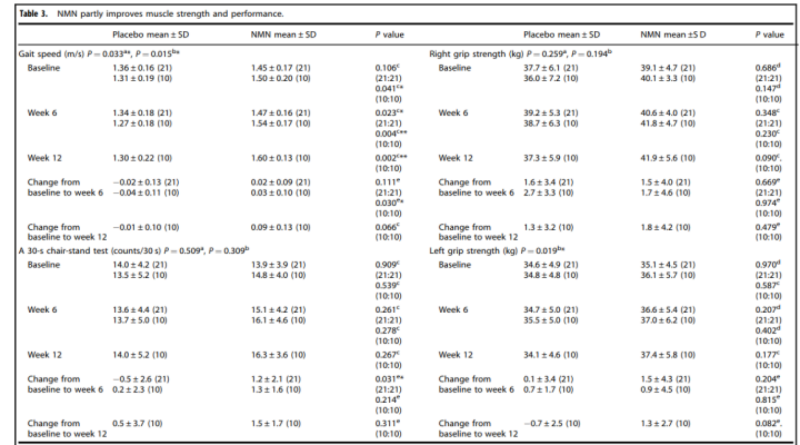
A clinical study at the University of Tokyo’s Graduate School of Medicine enrolled 42 healthy older men who received either 250 mg NMN or a placebo daily for 6 or 12 weeks [4]. Assessments included gait speed, a 30-second chair-stand test, and handgrip strength.
Results showed that NMN supplementation led to significant improvements in both upper and lower limb strength and walking speed, with noticeable effects as early as 6 weeks. Long-term supplementation also elevated NAD⁺ levels, suggesting NMN could be a potential strategy for managing age-related muscle decline.
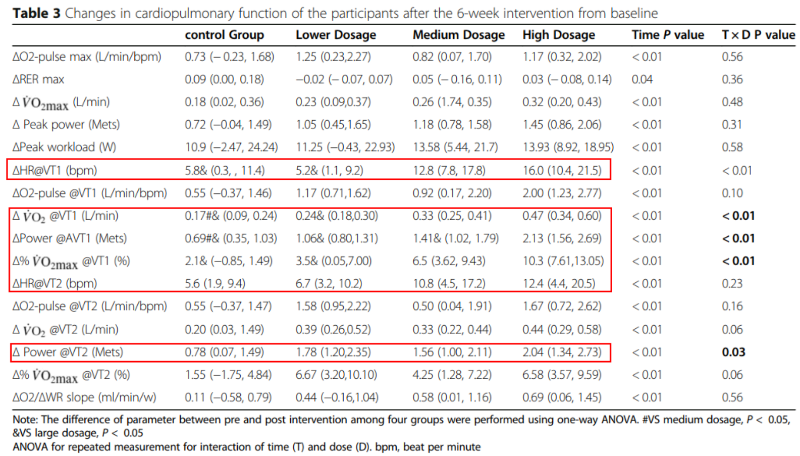
Another randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial conducted at Guangzhou Sport University involved 48 amateur runners aged 25–45 [5]. Participants were assigned to four groups receiving 300 mg, 600 mg, or 1200 mg NMN, or placebo, daily for 6 weeks, alongside 5–6 weekly training sessions (40–60 minutes each).
The study found that at 600 mg and 1200 mg, oxygen uptake at ventilatory threshold 1 (VT1) significantly increased, with greater improvements at higher doses. Energy expenditure at both VT1 and VT2 also rose, indicating better skeletal muscle oxygen utilization and improved aerobic performance.
In both studies, NMN supplementation (250–1200 mg/day) was well tolerated with no reported adverse effects [4][5]. This aligns with other human trials suggesting NMN is safe for short-term use within studied dose ranges.
While more long-term studies are needed, current evidence suggests that NMN supplementation—especially when combined with regular exercise—may help improve muscle strength, aerobic capacity, and endurance in adults. These findings highlight NMN’s potential role in supporting age-related muscle health and offer a promising direction for further research.
Muscle strength and endurance naturally decline with age, but the research reviewed here provides actionable insights: combining scientifically supported supplementation with appropriate exercise may help slow this process.
For companies and consumers interested in NMN, it is important to stay informed about product quality and safety standards, as well as developments in research. At Leadsynbio, we follow these studies closely to understand emerging trends and potential applications, providing guidance grounded in scientific evidence while contributing to the broader conversation on healthy aging and performance.
Disclaimer: Information derived from publicly available studies for educational purposes only. Not intended as medical or commercial advice. Proprietary images (if used) require direct rights-holder permission. Unauthorized reproduction prohibited.
[1] Dennison EM, Sayer AA, Cooper C. Epidemiology of sarcopenia and insight into possible therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13(6):340-347.
[2] Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Sayer AA. Sarcopenia. Lancet. 2019;393(10191):2636-2646.
[3] Liu J, Ding QQ, Zhou BY, et al. Expert consensus on diagnosis and treatment of sarcopenia in older adults in China (2021). Chinese Journal of Geriatrics. 2021;40(8):943-951.
[4] Masaki Igarashi, Masaomi Miura, Yoshiko Nakagawa-Nagahama, et al. Chronic nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation elevates blood NAD⁺ levels and alters muscle motility in healthy old men. Research Square (Preprint). 2021. DOI:10.21203/rs.3.rs-455083/v1.
[5] Liao B, Zhao Y, Wang D, et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation enhances aerobic capacity in amateur runners: a randomized, double-blind study. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2021;18:54.
Next:How Much NMN Should You Take? A Review of Global Clinical Trials
Prev:Science Publishes Clinical Trial Results: NMN Improves Muscle Insulin Sensitivity

Suzhou Leadsynbio Technology Co.,Ltd. is honored to be recognized inthe Hurun Future Unicorns – China Cheetahs Index 2025. This prestigious list spotlights our continued commitment to innovation and excellen...
[ Details ]Feb 09,2026