Menopause (perimenopause) typically occurs between ages 45-55. As women enter this phase, declining estrogen and progesterone levels can trigger physical and emotional symptoms like hot flashes, night sweats, and mood swings. Menopause also increases risks for health issues including osteoporosis and heart disease. A clinical study by Kyoto Doshisha University investigated NMN supplementation in postmenopausal women. Seventeen healthy participants (average age: 55) took 300mg NMN daily after breakfast for 8 weeks to evaluate NMN's clinical significance.

1. Enhanced Hormone Levels & Hormonal Health
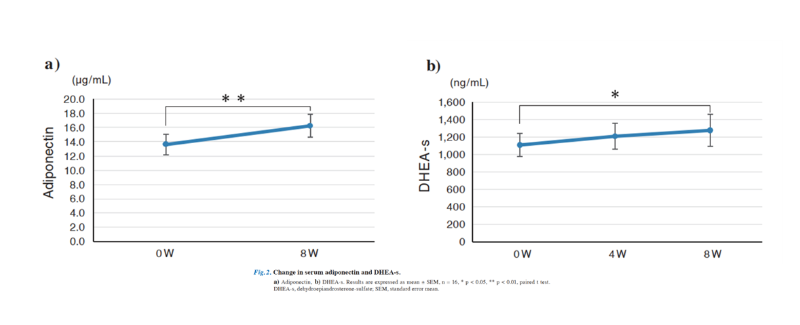
The trial showed that levels of Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate (DHEA-s)—often called the "anti-aging hormone"—significantly increased from 1,108 ng/ml to 1,275 ng/ml after NMN intake. DHEA, an endogenous steroid hormone, serves as an indirect precursor to estradiol and testosterone, offering unique anti-aging benefits distinct from sex hormones.
DHEA primarily circulates as DHEA-s in humans. Blood DHEA peaks between ages 20-30 and declines sharply by age 60. Low DHEA-s in postmenopausal women may contribute to multiple health concerns. Notably, NMN supplementation increased DHEA-s without affecting sex hormones (estradiol, free testosterone) or thyroid hormones, reaffirming NMN’s safety profile.
2. Improved Glucose & Cholesterol Metabolism
After NMN intake:
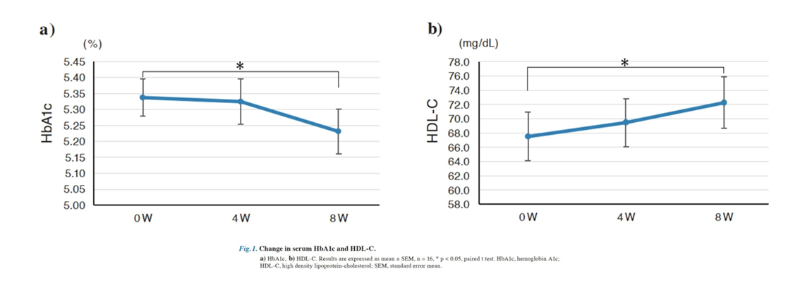
HbA1c decreased significantly from 5.34% to 5.23%, indicating better blood sugar control. HDL-C rose significantly from 67.5 mg/dL to 72.3 mg/dL.
HDL-C absorbs excess cholesterol, transporting it to the liver for breakdown. Higher HDL-C levels signal improved cholesterol metabolism.
3. Increased Adiponectin to Counter Lifestyle-Related Diseases
Adiponectin levels significantly rose from 13.6 μg/mL to 16.2 μg/mL (*p* = 0.004). This insulin-sensitizing protein, secreted by fat cells, is a known predictor of Type 2 diabetes and coronary heart disease. Clinical studies highlight its anti-diabetic, anti-atherosclerotic, and anti-inflammatory potential.
4. Enhanced Immune Function
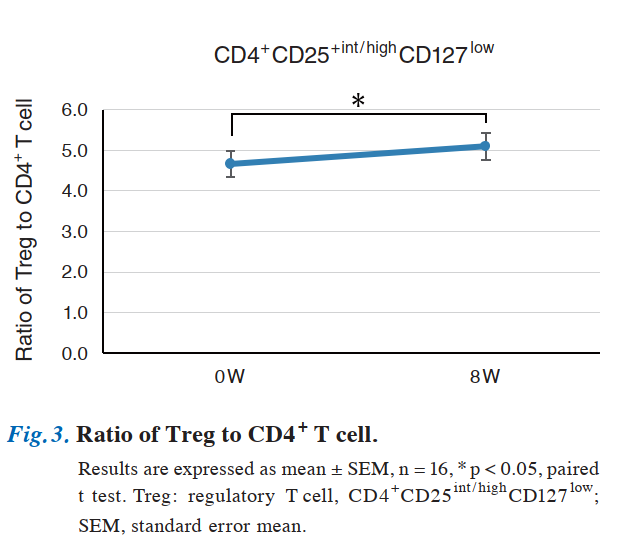
Narrow-spectrum regulatory T cells (CD4+CD25int/highCD127low), critical for immune regulation, increased significantly from 4.66% to 5.10% (within CD4+ cell area), indicating strengthened immunity.
5. Reduced Skin Glycation – A Potential Reversal of Skin Aging
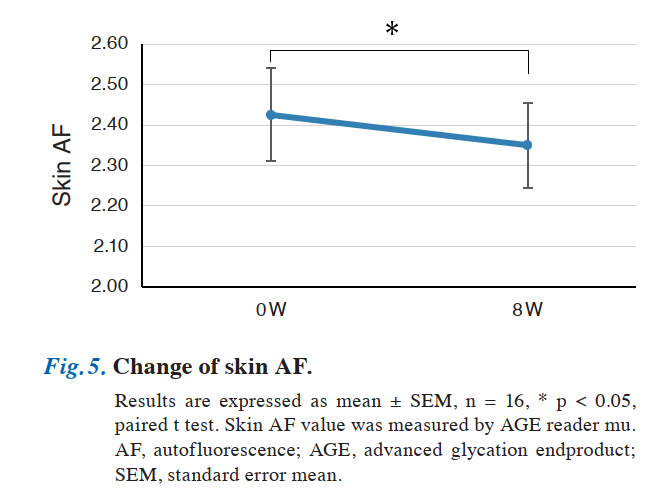
Skin autofluorescence (AF) values—reflecting advanced glycation end products (AGEs)—declined from 2.43 to 2.35.
With age, slowed metabolism and lifestyle factors cause sugar accumulation. This triggers glycation, where sugars bind to collagen, forming AGEs. AGE buildup causes skin aging, sagging, and dullness. Reduced AF values post-NMN suggest suppressed glycation. VASA skin evaluations also noted significant improvements in six areas: hydration, dryness, spots, firmness/elasticity, makeup application, and texture.
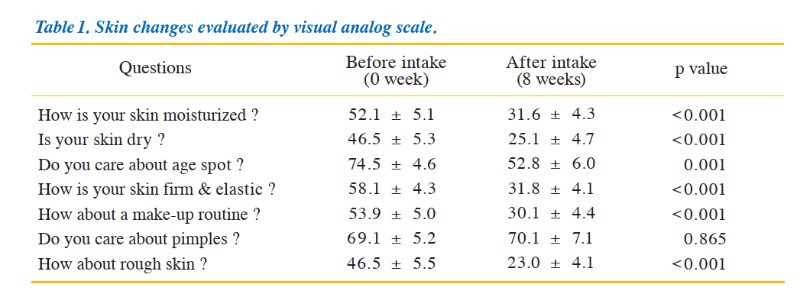
6. Subjective Physical Improvements
Participants reported significant improvements in skin condition, sleep quality, and fatigue levels.

This study demonstrating NMN's ability to improve multiple health markers in postmenopausal women provides new possibilities for evidence-based management of menopause.
The high-quality development of the NMN sector relies on sustained, collaborative efforts in fundamental and applied research across scientific and industrial stakeholders. Raw material quality remains a critical determinant of product safety and performance.
As a trailblazing NMN raw material supplier, Leadsynbio champions innovation through synthetic biology. Having undergone three generations of process refinement, our proprietary full-enzymatic synthesis technology delivers green, high-efficiency NMN production. This process has achieved scaled-up manufacturing, ensuring stable, traceable NMN supply from source.
We remain committed to advancing process innovation, continuously enhancing product quality and batch consistency to empower clients in building distinctive competitive advantages and collectively drive responsible industry growth.
Disclaimer: All information in this article is derived from publicly available sources. The content is shared for educational purposes only and does not constitute any form of medical advice or commercial recommendation. Should any infringement occur, please contact the author(s) for removal. No institution or individual may reproduce, republish, or quote any part of this material in any form without the express written consent of the Company. Where permission for citation or publication is granted, such use must strictly comply with the scope authorized by the Company.

Suzhou Leadsynbio Technology Co.,Ltd. is honored to be recognized inthe Hurun Future Unicorns – China Cheetahs Index 2025. This prestigious list spotlights our continued commitment to innovation and excellen...
[ Details ]Feb 09,2026